Design and teach a course
Horizontal and vertical alignment tools and Bloom's taxonomy
There are a number of taxonomies that provide
effective structures for designing alignment. You can see more detail about
these taxonomies (also often called 'models') in the table of contents to the
left.
However, most of the models are founded in the most famous of all - Blooms Cognitive taxonomy. This taxonomy was produced by a group which also produced two other taxonomies: the Affective domain taxonomy, and the Psycho-motor domain taxonomy. The differences between the three are toulined below:
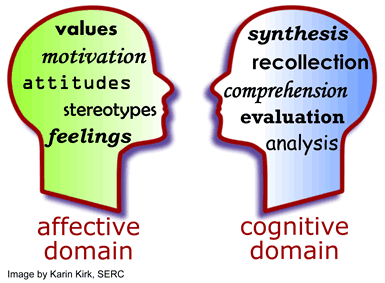
- The cognitive domain is about thinking / conceptualisation (see Anderson's taxonomy below).
- The affective domain deals with ethics, values and behaviours, which are very hard to measure.
- The psycho-motor domain deals with motor / muscular skills and things like dance and creative movement
The image to the right is sourced from https://serc.carleton.edu/details/images/7767.html.
Bloom's cognitive domain (Bloom's Taxonomy 1956)
- Knowledge: Remembering or retrieving previously learned material. Examples of verbs that relate to this function are: know, identify, relate, list, record, name, recognize, acquire
- Comprehension: The ability to grasp or construct meaning from material. Examples of verbs that relate to this function are: restate, locate, report, recognize, explain, express, illustrate, interpret, draw, represent, differentiate
- Application: The ability to use learned material, or to implement material in new and concrete situations. Examples of verbs that relate to this function are: apply, relate, develop, translate, use, operate, practice, calculate, show, exhibit, dramatize
- Analysis: The ability to break down or distinguish the parts of material into its components so that its organizational structure may be better understood. Examples of verbs that relate to this function re: analyze, compare, probe, inquire, examine, contrast, categorize, experiment, scrutinize, discover, inspect, dissect, discriminate, separate
- Synthesis: The ability to put parts together to form a coherent or unique new whole. Examples of verbs that relate to this function are: compose, produce, design, assemble, create, prepare, predict, modify, tell, propose, develop, arrange, construct, organize, originate, derive, write, propose
- Evaluation: The ability to judge, check, and even critique the value of material for a given purpose. Examples of verbs that relate to this function are: judge, assess, compare, evaluate, conclude, measure, deduce, validate, consider, appraise, value, criticize, infer
.
Bloom's affective domain
|
Category or 'level' |
Behavior descriptions |
Examples of experience, or demonstration and evidence to be measured |
'Key words' (verbs which describe the activity to be trained or measured at each level) |
|
1. Receiving |
Open to experience, willing to hear |
Listen to teacher or trainer, take interest in session or learning experience, take notes, turn up, make time for learning experience, participate passively |
Ask, listen, focus, attend, take part, discuss, acknowledge, hear, be open to, retain, follow, concentrate, read, do, feel |
|
2. Responding |
React and participate actively |
Participate actively in group discussion, active participation in activity, interest in outcomes, enthusiasm for action, question and probe ideas, suggest interpretation |
React, respond, seek clarification, interpret, clarify, provide other references and examples, contribute, question, present, cite, become animated or excited, help team, write, perform |
|
3. Valuing |
Attach values and express personal opinions |
Decide worth and relevance of ideas, experiences; accept or commit to particular stance or action |
Argue, challenge, debate, refute, confront, justify, persuade, criticize, |
|
4. Organizing or Conceptualizing Values |
Reconcile internal conflicts; develop value system |
Qualify and quantify personal views, state personal position and reasons, state beliefs |
Build, develop, formulate, defend, modify, relate, prioritize, reconcile, contrast, arrange, compare |
|
5. Internalizing or Characterizing Values |
Adopt belief system and philosophy |
Self-reliant; behave consistently with personal value set |
Act, display, influence |
Adapted from http://serc.carleton.edu/NAGTWorkshops/affective/index.html
The psychomotor domain
Bloom never completed the Psychomotor Domain. The most recognised version (below) was developed by Ravindra H. Dave.
|
Category or 'level' |
Behavior Descriptions |
Examples of activity or demonstration and evidence to be measured |
'Key words' (verbs which describe the activity to be trained or measured at each level) |
|
Imitation |
Copy action of another; observe and replicate |
Watch teacher or trainer and repeat action, process or activity |
Copy, follow, replicate, repeat, adhere, attempt, reproduce, organize, sketch, duplicate |
|
Manipulation |
Reproduce activity from instruction or memory |
Carry out task from written or verbal instruction |
Re-create, build, perform, execute, implement, acquire, conduct, operate |
|
Precision |
Execute skill reliably, independent of help, activity is quick, smooth, and accurate |
Perform a task or activity with expertise and to high quality without assistance or instruction; able to demonstrate an activity to other learners |
Demonstrate, complete, show, perfect, calibrate, control, achieve, accomplish, master, refine |
|
Articulation |
Adapt and integrate expertise to satisfy a new context or task |
Relate and combine associated activities to develop methods to meet varying, novel requirements |
Solve, adapt, combine, coordinate, revise, integrate, adapt, develop, formulate, modify, master |
|
Naturalization |
Instinctive, effortless, unconscious mastery of activity and related skills at strategic level |
Define aim, approach and strategy for use of activities to meet strategic need |
Construct, compose, create, design, specify, manage, invent, project-manage, originate |
Adapted from http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/Bloom/psychomotor_domain.html