MATLAB
4. Arrays
Array Subscripts
Given an array, you may need to access only one or some of the individual elements contained in the array, rather than the whole array itself. If A is an array with n elements in it, and i is an integer such that 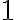 ≤
≤ 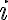 ≤
≤ 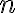 , then in Matlab A(i) is the
, then in Matlab A(i) is the 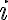 th element in the array (often denoted by Ai in mathematics).
th element in the array (often denoted by Ai in mathematics).
To illustrate this, enter the following into an M-file and then execute it. Firstly you will construct an array containing 9 random numbers between 0 and 1. Then you will use these elements of A to introduce scalar variables or new arrays which are merely sub-arrays of A. In each case the new variable names before the “=” signs have been suggested so that you can read the output conveniently. Please study carefully the expressions following the “=” signs as they are commonly used.
A=rand(1,9)
% the next two lines define scalar variables
a1=A(1)
a7=A(7)
% the remaining lines define new arrays
a3456=A(3:6)
a1357=A(1:2:7)
a852=A(8:-3:2)
Exercise 1: After executing the above M-file, what would you expect to see if you now entered each of the following after the prompt? Because we have not allocated a variable name for either expression, both of course will be named ans by default.
a852(3)
a1357(2:3)
Exercise 2: The MATLAB command
Q=linspace(0,100,141);
creates an array which has 140 subintervals and 141 points. Print out only
- the 46th element of Q
- the first four elements of Q
- the last three elements of Q.
Special array functions: sum, prod, length, max, min, sort, find, diff
The functions sum, prod, length, max, min, sort, find of an array are self explanatory by creating and executing the following in an M-file (do not type in the comment statements). diff(Z) is a new array containing the differences between consecutive elements of Z.
clear all
% create an array with 11 elements,
% each of which is a random number between 0 and 5
Z=5 * rand(1,11)
Zsum=sum(Z)
Zprod=prod(Z)
Zlength=length(Z)
% ’max’ finds the maximum value and its subscript (index) number
[Zmax,i] = max(Z)
[Zmin,j] = min(Z)
% ’sort’ and ’find’ create new arrays
Znew=sort(Z)
Zbig=find(Z>3.0) % for example, finds subscripts where Z(i) is >3.0
Znewbig=find(Znew>3.0) % have now moved to end of array