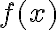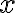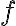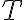Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
I |
|---|
Invariance and equivariance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
A function of an input is invariant to a transformation if In other words, function in invariant to transformation if produces the same output regardless of the output of [Pri23, §10.1]. For example, an image classifier should be invariant to geometric transformations of an image. A function of an input is equivariant or covariant to a transformation if In other words, function is equivariant or covariant to transformation if the output of changes in the same way under as the input[Pri23, §10.1]. For example, when an input image is geometrically transformed in some way, the output of an image segmentation algorithm should be transformed in the same way. References
| ||||